Embedded Finance (EF) is one of the biggest trends in financial services, accelerating innovation in the customer journeys of companies across multiple sectors.
But, what exactly is embedded finance?
This blog aims to serve as a practical, comprehensive guide to EF, with examples of its applications and benefits, a look at the underlying technologies powering the products, and the key challenges and considerations that any business considering EF should understand.
What is embedded finance?

Writing in Forbes, Finance Council Member Dmitry Dolgorukov defines embedded finance as “the use of financial tools or services — such as lending or payment processing — by a non-financial provider”. He adds: “Embedded finance is designed to streamline financial processes for consumers, making it easier for them to access the services they need when they need them.”
EF allows customers to access a wide range of banking products and services without having to leave the brand’s ecosystem; the EF use case many consumers are familiar with is instant payments, an example is when payment for a ride-sharing service happens automatically within the app once the journey is completed.
While embedded finance and Banking-as-a-Service (BaaS) are closely linked, it is important to distinguish between the two concepts. In their ‘Embedded Finance and Banking-as-a-Service Report 2023’, The Paypers explains: “EF and BaaS have a close relationship. One way to understand this is to recognise that Embedded Finance is enabled by BaaS. Embedded Finance takes the comprehensive BaaS model and presents it as an integrated financing option for consumers who are using other products or services … BaaS serves as the rock-solid infrastructure upon which the dynamic and innovative embedded finance offerings thrive.
“Embedded Finance transforms the customer experience. It’s the front-end magic that takes shape, putting the power of financial services right into the hands of the end users. Imagine a world where financial tools blend seamlessly into the apps and platforms you already love and use daily. No longer confined to traditional banking institutions, this fusion of BaaS and Embedded Finance disrupts the status quo, propelling us into a realm of unprecedented convenience and accessibility.”
How are different sectors leveraging embedded finance?

Embedded finance offers a competitive advantage to companies in a variety of sectors, with business leaders pursuing the opportunities it provides to enhance user experience, increase basket size, retain clients and create new revenue streams.
EF gives access to financial products when and where customers need them most. The integration of these contextual banking solutions creates a seamless customer journey that influences the browsing stage and helps to drive conversion. Consumers see the inherent value of these products, encouraging them to return to the brand. In turn, this strengthens customer loyalty and deepens their relationship with the business.
How Embedded Finance Benefits eCommerce Marketplaces
For adopters of EF solutions, new revenue streams are opened up, the costs to acquire and retain customers are significantly cut, and they are able to extend their product offering and business model into new areas.
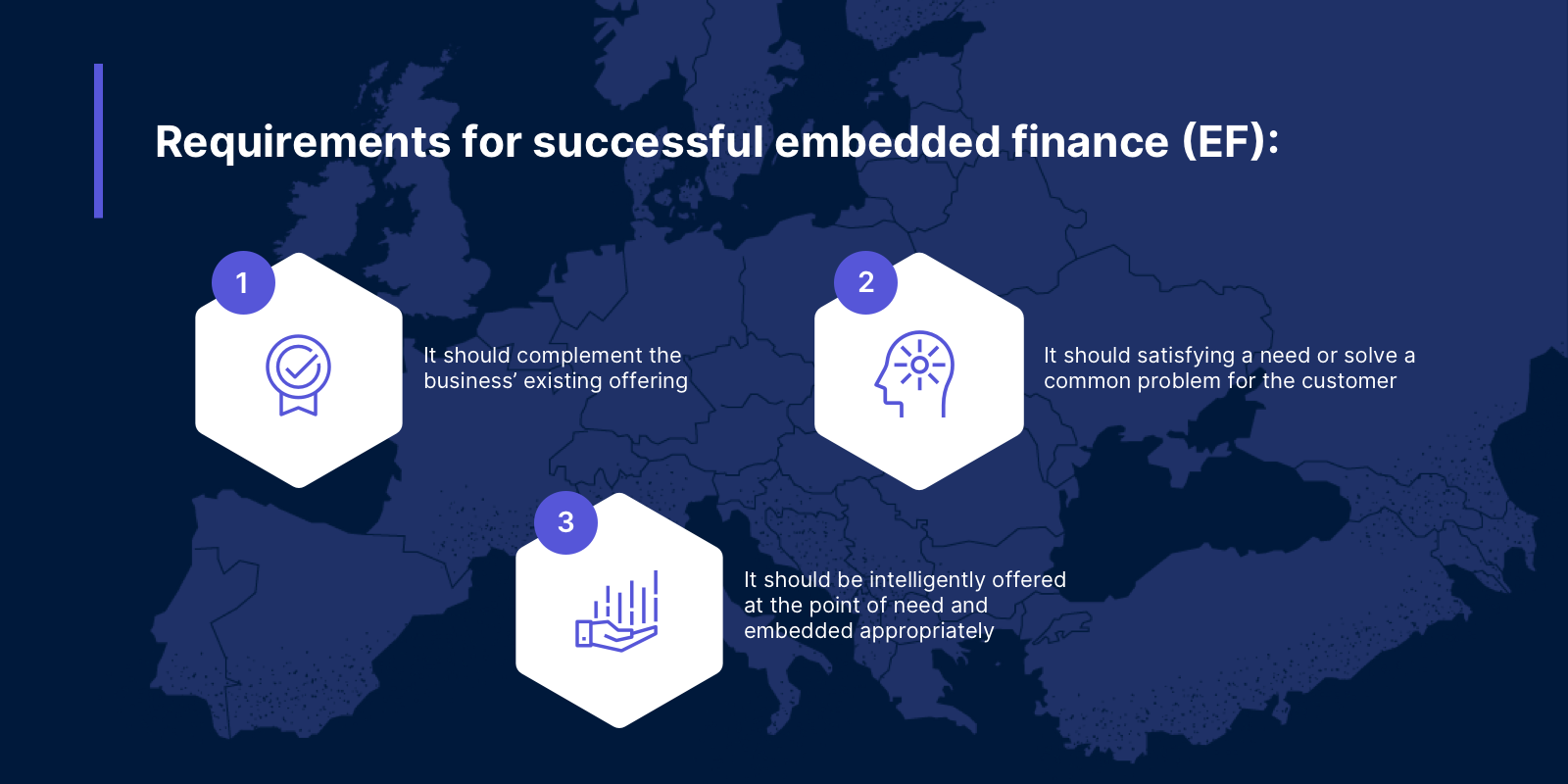
Successful EF requires three key things:
- It should complement the business’ existing offering, serving as a natural extension to their core products and services.
- It should make sense to the customer, satisfying a need or solving a common problem.
- Financial products should be intelligently offered at the point of need, embedded appropriately within the customer journey.
There have been a number of success stories in the retail space in recent years that demonstrate the advantages of properly implemented EF.
Starbucks
The Starbucks rewards platform is a powerful example of EF in action. The coffee giant’s app enables customers to load funds into their accounts, pre-order, pay for purchases and earn loyalty rewards. It boasts 28.7 million users in the US alone and was responsible for driving 55% of the company’s US operating revenue in Q4 2022.
Embedded Finance in the Retail Industry: Transforming the Customer Experience
Uber
Uber leverages embedded finance in various ways. For one, it gives its drivers access to other ride-hailing options like Bolt, Gett and Lyft, to increase their access to fares. The company also provides customised EF solutions to drivers, such as Uber cards and a digital wallet, allowing real-time access to earnings through the Uber Debit account.
Uber also replaced its traditional weekly payment system with an instant pay feature that gives drivers immediate access to their earnings after each trip. These EF solutions improve the drivers’ experience and provide financial convenience and flexibility, which allows Uber to retain more staff.
Five Predictions of how Embedded Finance will transform the Mobility Sector
Embedded finance and loyalty

While additional revenue sources are an obvious incentive for non-financial businesses to implement embedded finance solutions of their own, another appeal in boosting loyalty. By seamlessly integrating financial services into existing loyalty schemes, brands can supercharge customer engagement, boost stickiness and drive conversion.
This loyalty goes beyond traditional points-based systems, offering customers tangible benefits that make a real difference in their lives. In an era where consumers demand more personalised experiences, the incorporation of embedded finance provides an opportunity for brands to stand out by delivering a first-class customer experience and offering rewards that resonate with their audience.
As consumers increasingly seek value and meaningful rewards, embedded finance emerges as a strategic tool for brands to create a distinctive competitive advantage, fostering deeper connections with their customer base. This was underscored by Vodeno’s survey of over 3,000 European consumers in 2023, which found that two in five would only stay loyal to brands that offer EF benefits like Buy Now, Pay Later (BNPL) and cashback.
The role of technology in embedded finance

Technology plays a crucial role in enabling embedded finance. Cloud-based banking, smart contracts, APIs, big data and blockchain are instrumental in enabling EF, empowering businesses to navigate and capitalise on its transformative potential.
APIs are the fulcrum of BaaS provision and vital to EF, creating interfaces that allow the secure and speedy transfer of users’ personal data between brand and bank. Meanwhile, innovations such as cloud-based banking provide a scalable and secure foundation for EF; blockchain ensures security and transparency for transactions; and smart contracts offer cutting-edge efficiency and streamlining to processes.
In the realm of EF, the technical ability to seamlessly integrate into any front-end is paramount. The above technological components, as well as scalable BaaS infrastructure, have paved the way for greater flexibility in the provision of financial solutions to third parties. For example, the Vodeno Cloud Platform is a cloud banking system designed with a customer-centric approach that is able to seamlessly integrate embedded banking products into any customer journey, no matter their sector or specialty – this technology offers speed-to-market, with efficient delivery times of between six and 18 months.
Regulation and compliance of embedded finance

While the integration of EF presents numerous opportunities, it is essential to acknowledge and address the challenges and the risks that come along with it.
The most prominent challenge for an organisation seeking to implement EF is matching a solution to the specific needs of their customers. There is not a one-size-fits-all approach to EF, and businesses must understand their customer needs before identifying a solution to prioritise and develop.
Here are some important questions to consider:
- What pain points can a business solve for their customers through EF?
- Where are the areas in the customer journey that see drop off and can this be solved with EF?
- How can they leverage EF to build loyalty and repeat business among customers?

Compliance is also a key consideration. Compliance requirements can vary significantly from one BaaS product to another. While requirements are relatively light for simple payment processing solutions, lending solutions like BNPL loans are much more demanding due to changing regulations and the accountability and decision requirements for lending money to customers.
A compliant onboarding process is also critical. This vital procedure involves Know Your Customer (KYC) and Anti-Money Laundering (AML) checks, which must be executed with the utmost precision and security. What sets leading BaaS providers apart is their capability to tailor these processes to align seamlessly with the specific regulatory frameworks of different European countries.
How the BaaS provider is licensed will impact the types of products they can offer, as well as their responsibilities when it comes to regulation and compliance. Additionally, many BaaS providers delegate a lot of responsibilities to their BaaS partners, making it challenging to carry out regulatory oversight and monitor their partnerships properly.
It is important to understand if the BaaS provider has the expertise to handle compliance internally, as inadequate compliance support may drive you to explore alternative solutions. Outsourcing compliance or assembling an in-house compliance team are among the avenues you might consider. However, both options come with their complexities and costs.
Key takeaways on embedded finance
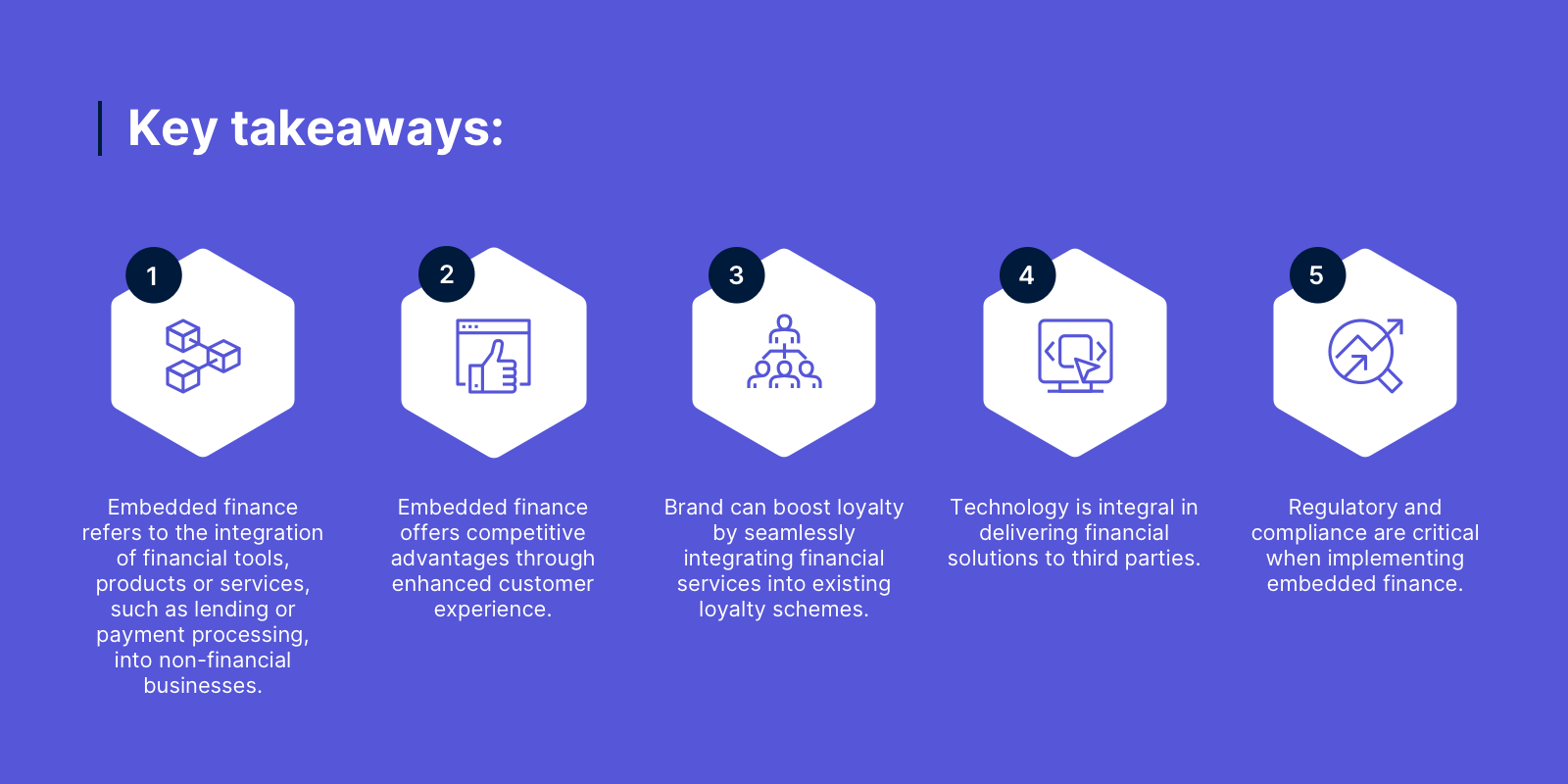
Let’s recap on the key takeaways Embedded Finance:
- What is it: Embedded finance refers to the integration of financial tools, products or services, such as lending or payment processing, into non-financial businesses. BaaS, meanwhile, is the delivery mechanism underpinning EF.
- Enhanced customer experience: EF offers competitive advantages across various sectors by enhancing user experience, increasing customer engagement, driving conversion, and creating new revenue streams.
- Boosting loyalty: By seamlessly integrating financial services into existing loyalty schemes, brands can supercharge customer engagement, boost stickiness and drive conversion.
- Tech is integral: Cloud-based banking, APIs, blockchain, and smart contracts are instrumental in enabling EF, providing scalability, security, efficiency and flexibility in delivering financial solutions to third parties.
- Regulatory and compliance: Challenges in implementing EF include matching solutions to specific customer needs, ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements (particularly in areas like KYC and AML), and ensuring end customers understand the products and their value.
The future of embedded finance

EF is transforming the financial services industry, offering new opportunities for both businesses and consumers. New products and use cases in different sectors are being developed every day – here we highlight some of the key trends we are seeing in the EF space.
With advancements in technology and the right regulatory framework, EF has the potential to revolutionise the way consumers and businesses interact with financial services and access the products they need.
As EF continues to reshape banking, businesses must fully understand its benefits and embrace the opportunities it presents. By partnering with BaaS providers that can offer the combination of technology, the right banking licence and regulatory and compliance expertise, companies can unlock the full potential of embedded finance.
If you are interested in hearing more about embedded finance and the solutions we offer, arrange a call with a member of the team today.


